Therefore, the costs assigned to the earliest units are charged to the cost of goods sold. The cost of ending inventory is determined by accounting for the acquisition costs of each item in the ending inventory. In other words, the problem is how an accountant can determine the acquisition cost or price paid for each item in the ending inventory when the items have been purchased at different times for different prices.

Physical Count:
Goods in transit include both sales on a FOB destination basis and purchases on a FOB shipping basis. During a period of rising prices or inflationary pressures, FIFO (first in, first out) generates a higher ending inventory valuation than LIFO (last in, first out). Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. Even with a well-developed electronic recordkeeping system, it is difficult—if not impossible—for these types of businesses to determine the price of each item remaining in the ending inventory. Or imagine a department store that sells a variety of products in different sizes and styles, again purchased at different prices.
Inventory Balance Cost per Inventory # of units unit Balance 680 at $40.00 $27,200.00
The specific identification method involves individually identifying and tracking the cost of each item in inventory. This method is typically used for high-value or unique items where it is practical to track their specific costs. After the quantity of items is determined, a particular cost flow pattern is assumed, and prices are attached to each item in the inventory. The total of the prices times the quantity equals the cost of the ending inventory.
Perpetual FIFO, Perpetual LIFO
The value of ending inventory can be calculated using different methods, such as the first in, first out (FIFO), last in, first out (LIFO), and weighted-average cost methods. Ending inventory is the value of goods still available for sale and held by a company at the end of an accounting period. The dollar amount of ending inventory can be calculated using multiple valuation methods.
Weighted-Average Costing:
For retailers, ending inventory is the value of products that have been purchased but not sold. That is to say, an assumption is made that costs flow in any one of four different patterns, regardless of how the goods physically move into and out of the firm. However, even after determining the quantity of the ending inventory, figuring out what to include in the acquisition cost is a major accounting problem that has still not been resolved. Indirect costs such as selling and warehouse expenses are not included in the cost of inventory due to the difficulty in reasonably allocating them to particular items.
- Specificidentification inventory methods also commonly use a manual form ofthe perpetual system.
- Normally, no significant adjustments are needed at the end of the period (before financial statements are prepared) since the inventory balance is maintained to continually parallel actual counts.
- Electronic product codes (EPCs) such as radio frequency identifiers (RFIDs) are essentially an evolved version of UPCs in which a chip/identifier is embedded in the EPC code that matches the goods to the actual batch of product that was produced.
- The total of the prices times the quantity equals the cost of the ending inventory.
- The credit entry to balance the adjustment is $13,005, which is the total amount that was recorded as purchases for the period.
Total March 15
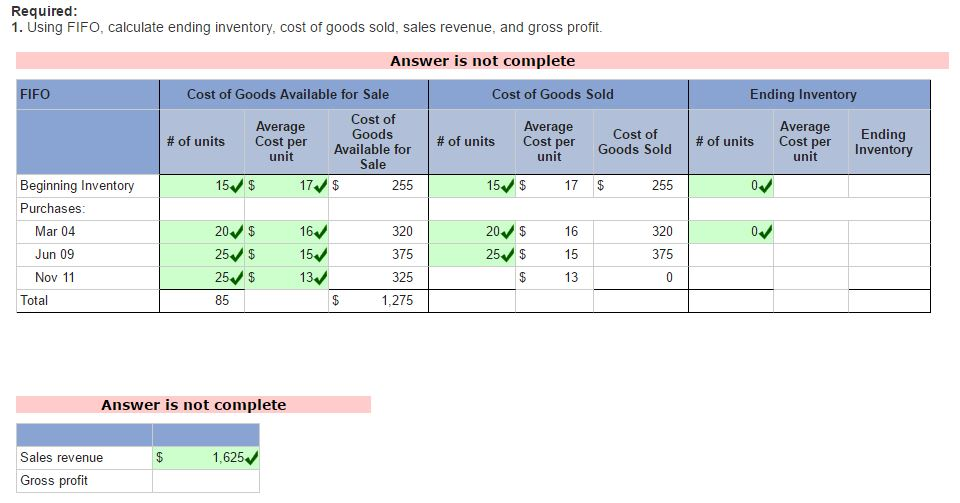
The cost of goods sold, inventory, and gross margin shown in Figure 10.7 were determined from the previously-stated data, particular to FIFO costing. The specific identification costing assumption tracks inventory items individually, so that when they are sold, the exact cost of the item is used to offset the revenue from the sale. The cost of goods sold, inventory, and gross margin shown in Figure 10.5 were determined from the previously-stated data, particular to specific identification costing. The specific identification costing assumption tracks inventory items individually so that, when they are sold, the exact cost of the item is used to offset the revenue from the sale.
The credit entry to balance the adjustment is $13,005, which is the total amount that was recorded as purchases for the period. Ending inventory, also known as closing inventory, refers to the total value of goods that a company has available for sale at the end of an accounting period. It is a key component in the calculation of the cost of goods sold (COGS) and is essential for determining a company’s profitability.
Let’s return to the example of The Spy Who Loves You Corporation to demonstrate the four cost allocation methods, assuming inventory is updated at the end of the period using the periodic system. It is important to note that the specific formula for calculating ending inventory may vary depending on the accounting software or method used. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various methods and techniques for calculating ending inventory. Whether you’re a small business owner or a finance purchases journal format calculation and example professional, understanding how to accurately calculate ending inventory is crucial for making informed financial decisions. If all items are purchased at the same price, there will be no problem in determining the cost of either the ending inventory or the items sold. For retailers, this means that acquisition costs include the purchase price less any sales discounts, plus other freight charges, insurance in transit, and sales taxes that are incurred to have the product ready for sale.
A physical inventory is required, regardless of whether a firm uses the perpetual or the periodic inventory method. Inventory may also need to be written down for various reasons including theft, market value decreases, and general obsolescence in addition to calculating ending inventory under typical business conditions. Inventory market value may decrease if there is a large dip in consumer demand for the product. Similarly, obsolescence may occur if a newer version of the same product is released while there are still items of the current version in inventory. This type of situation would be most common in the ever-changing technology industry. It is essential to report ending inventory accurately, especially when obtaining financing.
The credit entry to balance the adjustment is for $13,005, which is the total amount that was recorded as purchases for the period. This entry distributes the balance in the purchases account between the inventory that was sold (cost of goods sold) and the amount of inventory that remains at period end (merchandise inventory). The inventory at period end should be $6,795, requiring an entry to increase merchandise inventory by $3,645.